
Computer Systems: Hardware, Software, and Brainware
What is a Computer System?
A computer is an electronic device designed to help solve problems faced by humans. For a computer to function, it must have three core components:
- Hardware
- Software
- Brainware (Humanware)
A system can be defined as a unit consisting of two or more components or subsystems that interact to achieve a goal. A computer is a system because its components are interdependent and interact with one another.
1. Hardware
Hardware refers to the physical components of the computer system. It is the tangible part that exists at the lowest level of the architecture.
Key examples of hardware include:
- Processor (The brain of the computer)
- Main Memory (RAM/ROM)
- I/O Devices (Input and Output devices)
The Processor
The processor is where program instructions are executed. It consists of:
- Control Unit (CU): Manages execution and controls all other components like memory and I/O modules.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs mathematical and logical operations.
- Registers: Temporary storage within the processor for instructions, data, and addresses.
Processor Instruction Types:
- Processor-Memory Data Exchange: Reading/writing to main memory.
- Processor-I/O Data Exchange: Reading/writing to peripheral devices via I/O modules.
- Data Processing: Arithmetical or logical operations.
- Instruction Flow Control: Operations such as jumping to a specific instruction.
Types of Registers:
- User Registers: Store data and addresses (Data Registers and Address Registers).
- Status and Control Registers: Control program execution.
- Program Counter (PC): Stores the address of the instruction being executed.
- Code Segment (CS): Stores the memory segment address.
- Instruction Register (IR): Stores the code of the instruction being executed.
- Flag Register (F): Stores the status resulting from an instruction (e.g., division by zero).

Main Memory
Main memory stores instructions and data that are currently being used or will soon be executed.
- ROM (Read Only Memory): Non-volatile memory, typically found in the BIOS on the motherboard. It handles core configurations like power management and boot sequences.
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Volatile storage used for data and programs currently being processed.

System Bus
The bus is the internal communication channel between components:
- Control Bus: Sends control signals (e.g., read/write).
- Address Bus: Sends the memory or I/O address being accessed.
- Data Bus: Transports the actual data or instructions.
Input and Output (I/O) Devices
- Input: Devices used to enter data (e.g., Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner, Webcam).
- Output: Devices used to display processed information (e.g., Monitor, Printer, Plotter).


2. Software
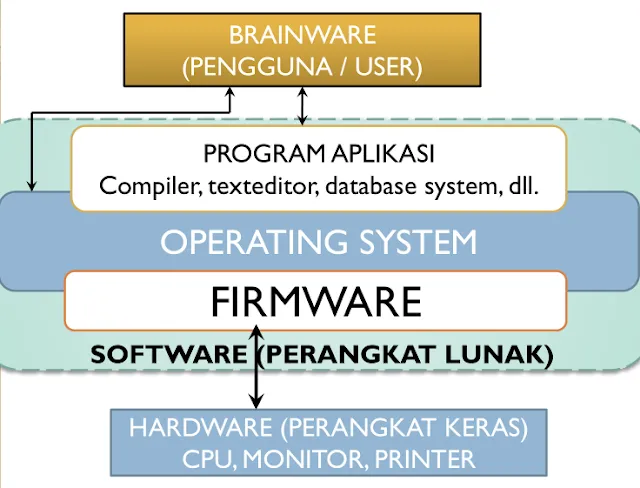
Software provides the instructions that tell the hardware what to do.
- Firmware: Software built into hardware by the manufacturer (e.g., BIOS).
- Operating System (OS): Manages all hardware and software resources (e.g., Windows, Linux, macOS). It provides the interface for both users and applications.
- Application Programs: Programs designed for specific user tasks (e.g., Microsoft Word for writing, WinAmp for music, WinZip for compression).
3. Brainware (The Users)
Brainware refers to the people who operate, program, and maintain the computer system.
- System Programmers: Highly skilled users who create operating systems or system-level software. They must understand hardware deeply.
- Application Programmers: Users who create specific applications that run on top of the OS (e.g., developers of accounting or word processing software).
- End Users: The people who use the computer to accomplish tasks using existing applications. They do not need deep technical knowledge of hardware or software systems.
That covers the fundamentals of a computer system. Without any one of these three—Hardware, Software, or Brainware—the computer would be unable to function as a tool for solving human problems.