
This is My Smart City, Where Is Yours??
Hello guys, welcome back to Kuasai Teknologi! My apologies for the long delay between updates. This time, I’ll be sharing my personal vision for a Smart City.
Technology is evolving rapidly, making information more accessible and facilitating interaction. A Smart City consists of several key components:
- Smart Home
- Smart Mobility
- Smart Retail
- Smart Health
- Smart Energy
- Smart Agriculture
- Open Data
- Internet of Things (IoT)
While there are many other components, I’ll focus on these eight and explain how they work according to my understanding.

1. Smart Home
A Smart Home uses a central controller to easily manage everything within the house.

Everything connected to the system can be controlled with a single tap. For example, CCTV cameras can be used to secure the home. When you leave, you simply activate the CCTV via a smartphone app. If the camera detects an intruder, it can trigger face detection. If the intruder is wearing a mask, the system can even attempt to detect fingerprints on objects they’ve touched. This data is then cross-referenced with Open Data.
2. Open Data
Open Data refers to public information like ID card data (KTP), vehicle registration (STNK/BPKB), or driver’s licenses (SIM) that is accessible to the public for specific verification purposes. It does not include highly sensitive private documents.
Access typically requires being an Indonesian citizen and logging in with a National ID Number (NIK).
Connection to CCTV:
In the Smart Home scenario, if a thief is caught on camera, the “face detection” data is automatically linked to the Open Data Database. The app then sends a report: “Name: [Name], NIK: [Number], Fingerprint: [Data] has committed a theft. Click for details.”
3. Smart Mobility
Smart Mobility involves “smart cars” equipped with distance sensors, weather sensors, automatic door locks, GPS trackers, and more.
Watch: Smart Mobility Video (Follow the link instructions for a look into future technology).
4. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT is arguably the most critical component, as most application scenarios discussed here rely on it. IoT ties the Smart City together.
5. Smart Health
Current hospital systems (especially in areas like Lombok, NTB) often require significant manual effort from nurses to monitor patients. Smart Health simplifies this.
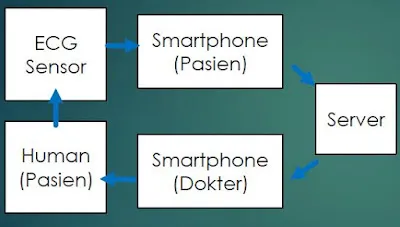

ECG sensors can detect changes in a patient’s condition and automatically alert the patient’s smartphone and the ICU monitor. The server then notifies the doctor via SMS or call. This ensures immediate attention. CCTV can also be used so patients can gesture for help (e.g., to use the restroom) without needing a nurse to be constantly present in the room.
6. Smart Energy
This involves the automatic use of electricity. For example, streetlights equipped with day/night sensors that turn off during the day and on at night. Solar panels are also a key part of this, helping both cities and remote areas save electricity.
7. Smart Traffic Control System (Pattern Recognition)
This uses CCTV programmed to recognize patterns on the road, ensuring safety and helping to prevent vehicle theft.
Unfortunately, this technology hasn’t been widely implemented in Indonesia yet. My hope in sharing this vision is that such systems will be adopted by the government in the future.
This concludes my vision for a Smart City. I hope this article is useful and contributes to a more technology-forward future. Thank you!